Object Definitions
Object Definitions control the data model in Farsight and can have one of the following origins:
- Introduced into the Workspace by an Extension deployment.
- Manually created custom Object Definition.
Create Object Definition
Section titled “Create Object Definition”-
Press the button NEW OBJECT DEFINITION.

-
Enter the designated name into the Object Name input field.

-
Optionally you can start defining Fields for your new Object straight away. See next section for additional details on Field creation by using the Field Editor.
-
Press the SAVE button in the right top corner to completed the process.
Every Object Definition comes with three system Fields and they are protected from being modified or deleted.

Manage Object Definition
Section titled “Manage Object Definition”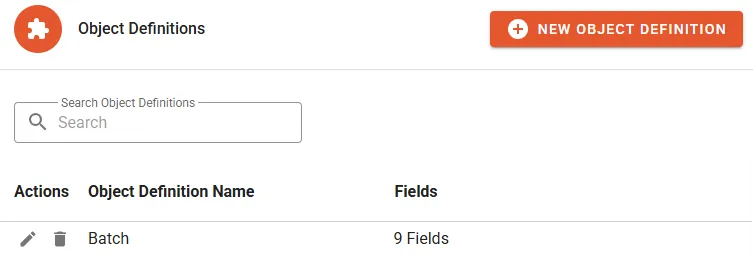
The Object Definitions presents the following details:
- Object Definition Name
- Fields is the total count of Fields (including system generated).
Actions
Section titled “Actions”- Edit to access editor mode and change properties or add/remove Fields/Choices.
- Delete to permanently remove the entire Object Definition.
Field Editor
Section titled “Field Editor”Create Field
Section titled “Create Field”-
Press the button NEW FIELD which will add a new Field element.


-
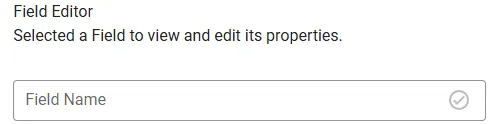
Define a Field Name for the new Field.
-
Select a type for the Field.

-
The Field types come with different options which is outlined in section Field Types.
Edit Field
Section titled “Edit Field”-
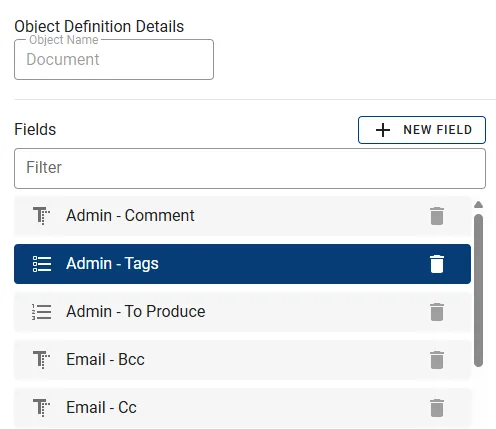
Select the designated Field in the list.
-
For Field type Basic, the Field Editor presents the full list of options below. Other field types might offer a reduced set or non of these options.

-
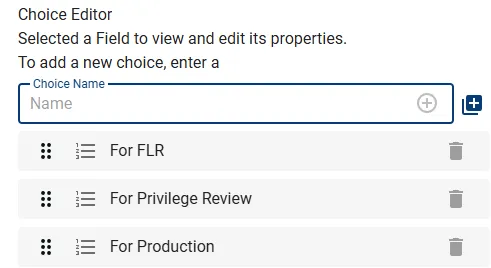
For Choice type Fields, the Choice Editor is displayed on the right side:
Field Types
Section titled “Field Types”Basic Types
Section titled “Basic Types”Basic types support the following properties:
- Field is Audited: All modifications to the field will be recorded in audit log.
- Field is Required: A value is mandatory for each record which means records cannot be stored or saved without having a value assigned.
- Field is Unique: The value needs to be unique for the record being stored or modified.
- Field is Relational: The content will be used to describe a relation to other records. Checking this option will unlock an additional input box Relation Name to describe the relation. Examples:
- A set of Documents sharing the same group identifier represent a family.
- A set of Documents sharing the same file hash represent a group of binary duplicates.
Text Fields can store up to 1 GB of text.
Date / Date & Time
Section titled “Date / Date & Time”- Date & Time: Typically used to store metadata dates including timestamp.
- Date: For dates with no time reference e.g. approval date or signing date.
Boolean
Section titled “Boolean”A simple Yes/No Field.
Decimal / Whole Number
Section titled “Decimal / Whole Number”- Decimal: Values with fractions e.g. account balance.
- Whole Number: Recommended for e.g. byte count or pieces.
File / Multi-File
Section titled “File / Multi-File”Can hold a single or multiple files.
Choices
Section titled “Choices”Choice based field types support the following property:
- Field is Audited: All modifications to the field will be recorded in audit log.
Choice
Section titled “Choice”This type is used for single decisions or distinct properties:
- Relevancy decision
- Classification
Multi-Choice
Section titled “Multi-Choice”Use this type if multiple Choices can be applied and co-exist:
- Flag foreign languages
- Assign custodians
Objects
Section titled “Objects”Object / Multi-Object
Section titled “Object / Multi-Object”This will create a Field which can reference another Object Definition. Use the additional input boxes to configure the linking: 
- Select the Related Object Definition to be linked by this Field.
- Select the Reverse Cardinality for the relation (One or Many).
- Related Field Name is defining the name for the Field to be registered on the target Object Definition.